Describe the Rate of Division of Cancer Cells
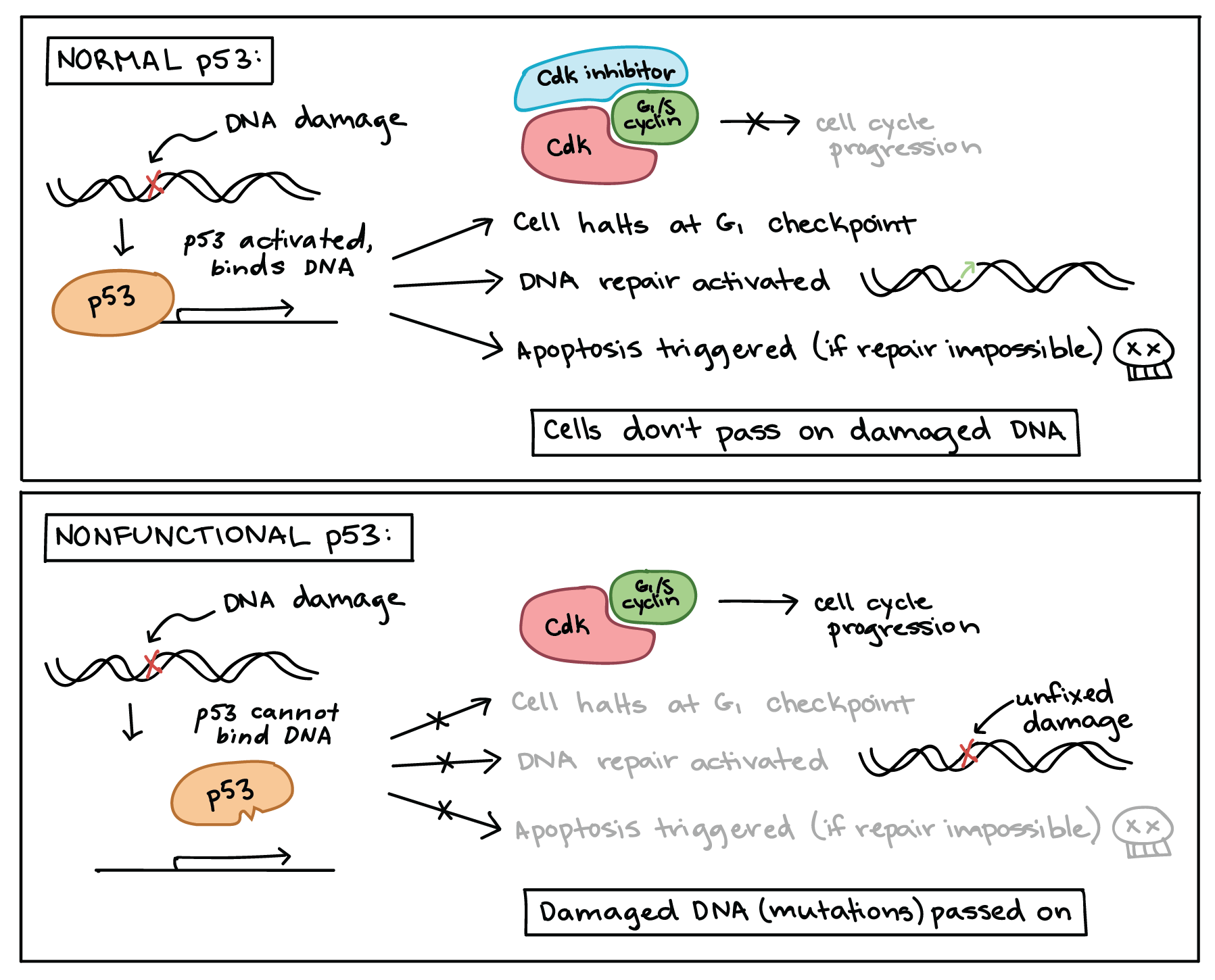
Mutations in genes can cause cancer by accelerating cell division rates or inhibiting normal controls on the system such as cell cycle arrest or programmed cell. In addition cancer cells often have an abnormal shape both of the cell and of the nucleus the brain of the cell The nucleus appears both larger and darker than normal cells.
Cancer And The Cell Cycle Biology Article Khan Academy
The S phase synthesis phase is period during which a cell.
. In cancer as a result of genetic mutations this regulatory process malfunctions resulting in uncontrolled cell proliferation. See answer 1 Best Answer. Normal cells have many controlling factors that allow them to divide on a regular basis or when needed but cancer cells have lost the ability to.
The mutations may be inherited or completely random. Basal cells divide faster than needed to replenish the cells being shed and with each division both of the two newly formed cells will often retain the capacity to divide leading to an increased number of dividing cells. In normal cells the cell cycle is controlled by a complex series of signaling pathways by which a cell grows replicates its DNA and divides.
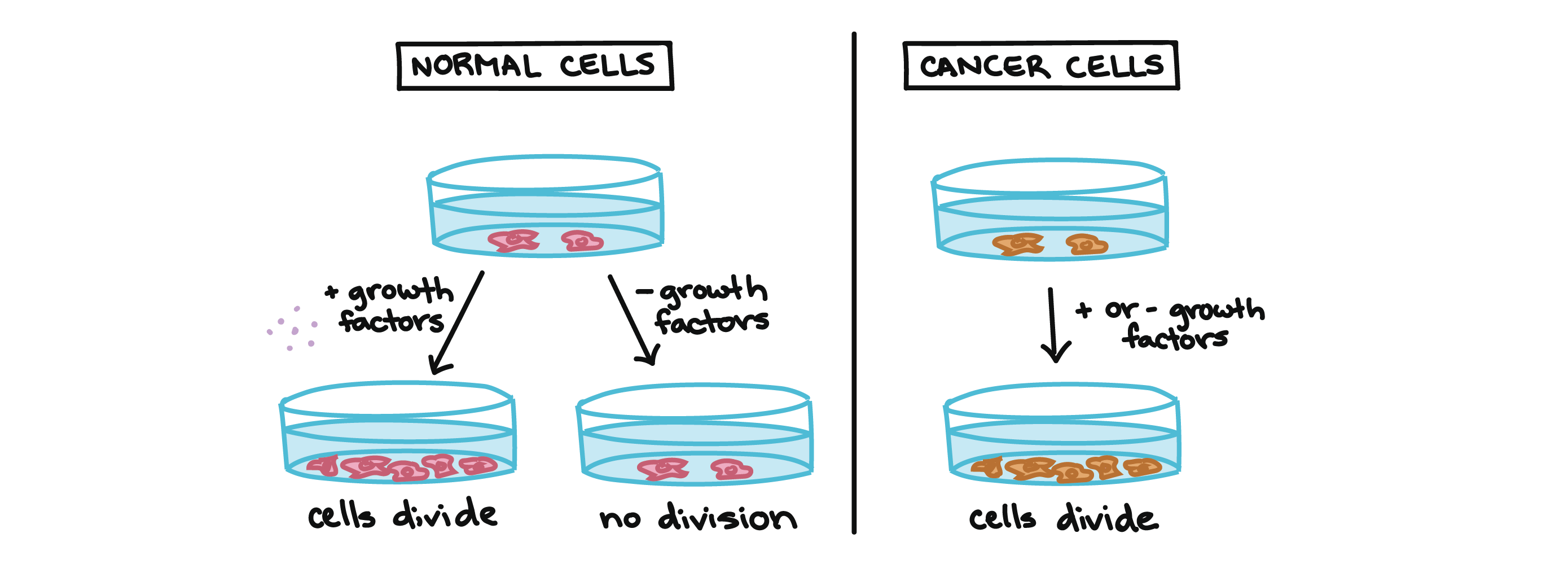
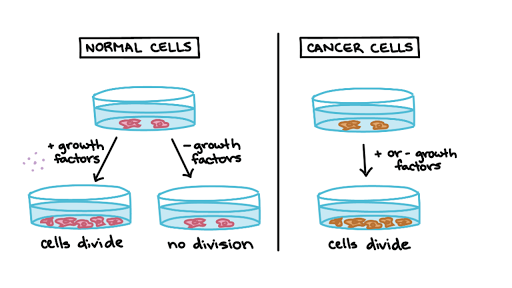
Describe the rate of division of cancer cells. Normally human cells grow and multiply through a process called cell division to form new cells as the body needs them. A Describe how EGF affects cell division.
How cancer can be linked to overactive positive cell cycle regulators oncogenes or inactive negative regulators tumor suppressors. Cancer can start almost anywhere in the human body which is made up of trillions of cells. A cell grows and carries out all normal metabolic functions and processes in a period called G 1 Figure 1.
Characteristics of Cancer Cells. In contrast to normal cells cancer cells often exhibit much more variability in cell sizesome are larger than normal and some are smaller than normal. What can cancer cells develop into.
Cancer cells can start to form when genes made up of DNA experience certain changes or mutations that cause the cells to behave abnormally. The cancerous cells would have a higher mitotic index as they divide more rapidly causing the dividing ratio of the cell cycle to be higher. Cancer is a group of diseases characterised by uncontrolled cell division which leads to growth of abnormal tissue.
The results published June 6 2018 in Nature suggest that by understanding how normal cells commit to cell division it may be possible to target this pathway in cancer cells and prevent them from dividing when they should not. B Identify the role of each experiment in determining the difference in how cancer and normal cells respond to EGF. Cancerous tumours are either malignant or benign.
These changes may be due to external factors such as tobacco smoke and ultraviolet rays. G1 phase gap 1 phase is the first gap or growth phase in the cell cycle. The single-cell origin of many tumors has been demonstrated by analysis of X chromosome inactivation Figure 152As discussed in Chapter 8 one member of the X chromosome pair is inactivated by being.
Cells no longer adhere together and they become slippery moving throughout the body Absence of cellular barriers. For cells that will divide again G 1 is followed by replication of the DNA during the S phase. To replace aging and worn cells the body primarily uses a process called mitosis in.
Creation of new blood vessels - advanced cancers can secrete angiogenic factors VEGF Lack of Cellular Adhesion. The Development of Cancer. Cancer is a disease in which some of the bodys cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body.
Cancer cells can activate telomerase unlimited division and proliferation Angiogenesis. The abnormality in cells can be progressive with a slow transition from normal cells to benign tumors to malignant tumors. Cell division and its role in cancer development.
Cancer cells grow and divide uncontrollably to form a mass of cancer. What 2 treatments have been developed to destroy cancer cells. Cancer cells grow and divide at an abnormally rapid rate are poorly differentiated and have abnormal membranes cytoskeletal proteins and morphology.
Compare the mitotic rates for each cell type. The transition to skin cancer begins when the normal balance between cell divisioncell loss is disrupted. Lets read more about cancer in vivo because it behaves completely different than immortalized cell lines in in vitro tests.
This means that a cancer is essentially a disease of mitosis. Rate of division. C Calculate the mitotic index number of cells in mitosis divided by total cells for each kind of cell.
Cancer is unchecked cell growth. Mitosis is a type of cell division which produces two identical diploid daughter cells. One of the fundamental features of cancer is tumor clonality the development of tumors from single cells that begin to proliferate abnormally.
So we can assume that 124h is the maximum rate of cell division by cancer. Cancer begins when a single cell is transformed or converted from a normal cell to a cancer cell. Originally tumours were thought to grow because they consisted of cells that multiplied more rapidly than cells in the surrounding tissue.
Cancer cells undergo uncontrolled cell growth. HOPE IT HELPS. Some tissues in the body have higher mitotic indexes than others because some parts of the body need to replicate their cells more.
Abnormal Cell Division.
What Is Cancer Precision Medicine Sib
Comments
Post a Comment